The Important Decisions You Have to Make When Buying Oxy-Fuel Torches
Even though there’s an ongoing discussion whether plasma-arc processes are better suited than laser processes for cutting and welding, oxy-fuel remains the most commonly utilized method worldwide. That is so simply because the equipment is robust, entry-level costs are quite modest, and it’s easy to use. You can find high-end oxy-fuel equipment for just a few hundred bucks, and you can rent the gas cylinders. Moreover, due to the fact that electricity isn’t needed for this process, it’s quite portable which means that you can cut and weld virtually anywhere.
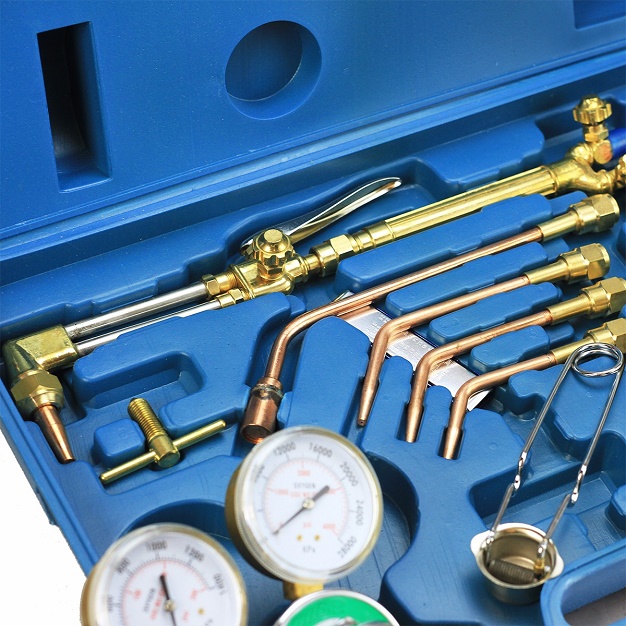

Moreover, there are many different cutting torches for sale, as well as welding nozzles, some of which are designed to remove the head of a rivet, while others to cut off the base of an l-beam. Moreover, some extend up to 24 inches from the torch, while others are made to cut at odd angles and fit into awkward places. In other words, there are oxy-fuel cutting torches for sale for every occasion.
But besides the type of torch, you need to consider the type of fuel that’s going to power the welder. There are two types of oxy-fuels available: acetylene and propylene.
- Acetylene is the most versatile and hottest oxy-fuel, and it can be used for every single purpose. It has a relatively short pre-heat time, as the flame temperature can be anywhere between 3000°C to 3500°C. However, this is the most expensive gas and is not very efficient for heating large areas.
- Propylene is a generic term used for various types of gases – ranging from gases that are propane mixed with ethylene or some other chemical to specific gases with a unique formula. Gauging, cutting and heating can all be performed very efficiently. However, it has longer pre-heat times, but that can be negated by using the right tip design. Propylene can reach temperatures anywhere from 2500°C to 3000°C. Propylene is typically not used for welding, only cutting, gauging and heating.
- Propane and natural gas have flame temperatures of 2000°C to 2500°C and are the most affordable gasses available. Propane, due to its high BTU output is the most efficient fuel for heating and its oftentimes accompanied by heavy, large heating tips. Similarly to propane, these gases aren’t used for welding, only cutting, gauging and heating.
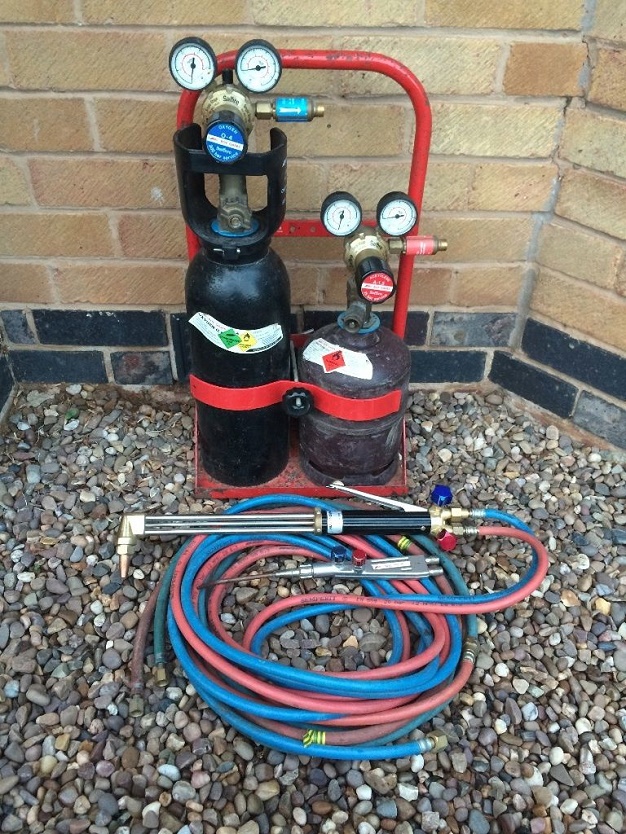

Ultimately, it all comes down to the type of application you’ll be using the torch and fuel for. Tips are designed for specific applications, and there are different tips used for gouging, heating and cutting. They can be a two-piece hybrid with a copper outer piece and a brass inner piece or a single piece of solid copper. Some tips are designed to be used with automated machinery for cutting, or high-pressure cutting which results in a cleaner, quicker, and more accurate cuts.